Do you want to improve your local business’ website, and lead more customers? By applying Schema Markup to your website, both Google bots and users can easily render and distinguish your website from others.
However, adding local schema can be hard, and always depends on the business category, and if your business has one or multiple locations targeted.
To make your schema choice and implementation easier, we will explain, what schema is and how you can apply it to your local SEO strategy.
What is Local Business Schema?
Schema is a type of structured data markup, which can be added to a website. The primary purpose of schema markup is to help search engine bots identify the type of content that exists on your page. Many types of schema exist, so choosing the correct one could improve your website’s current ranking position.
Adding Schema to your pages helps crawlers to better understand content, which also helps in optimizing your crawl budget, and crawl request handling.
The main content areas in each schema are:
@Type (business category) – Try choosing the category of your business. If your business category doesn’t exist in the list, you can always use local business.
Image (Image of the page) – Choose the image, which will be seen when your URL is shared on social media.
Phone (Company phone) – A phone number, which will be used for business inquiries.
Name (company name)
Description (Page offerings) – Explain what your page offers (e.g. product or service)
OpeningHours (operational hours) – Specify when the business is opening/closing, along with the working days.
URL (page URL) – The URL of the page, which will be accessed.
Address (physical location of the business) – The location where local customers can find the physical building and visit the local store, outlet, or even building.
Reviews – The average number of reviews, which is given on review websites.
AggregrateRating – The medium rating given by customers, which is shown on Google Business Profile, TrustPilot, and others.
Breadcrumb (Optional) – If your website uses breadcrumbs, adding them to your local schema template can help bots find more about your content.
PriceRange – The cost per service or product. Most businesses use the range of $ – $$$.
Websites that use schema often see their websites with rich snippets in the search results. Search engines find the most suitable links on the website, and use variations to fit the user’s needs.
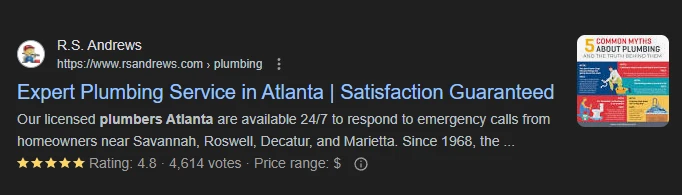
On the image you can see a thumbnail, rating, and price range being applied. These are called rich snippets and are used for informational purposes.
Based on these factors, many users can make an informed decision, about whether to purchase from the business.
How Local Schema Can Impact Rankings
Schema is a part of the technical SEO factors, which is considered a ranking factor, but its ranking boost is not significant. Yet, it’s an important aspect, recommended to have on your website.
When applied properly, and linked with a Google Business Profile, many local websites see higher rankings and better results.
For example, searching for “plumber in Atlanta” showed that the top 5 results have a proper schema applied on each page.
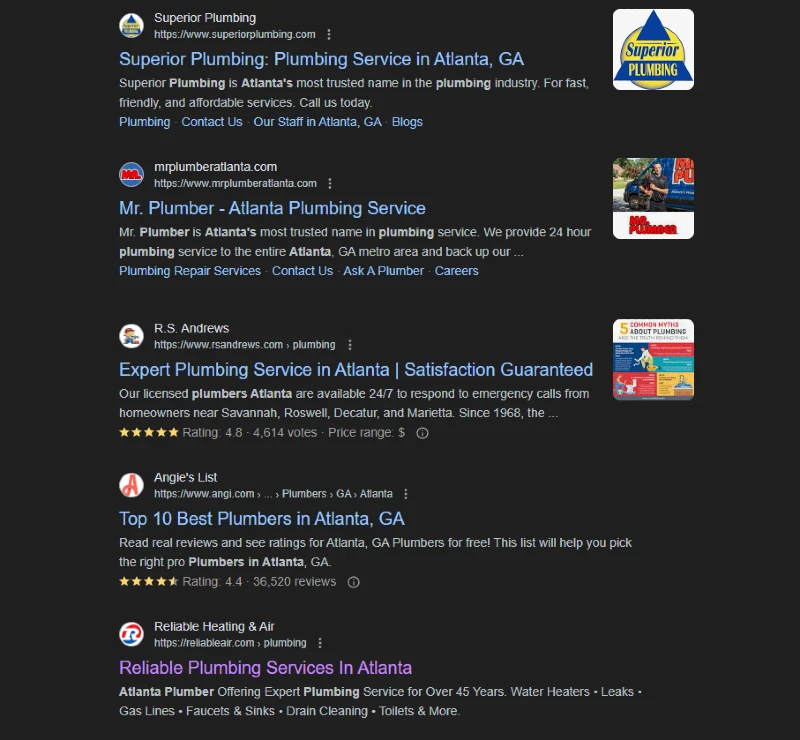
On top of that, the first 2 results have navigational links displayed instead of ratings, or price range. A reason for that is due to Google’s decision on what is considered helpful through user feedback.
Trying to replicate their schema in order to achieve the same result would not end up the same. After all, the display of your website in the search results is distinguished through thousands of local ranking factors, and cannot be changed by the user itself.
How Do I Implement Schema Markup On My Site?
1. Schema.org
The easiest place to generate schema and adjust it to your website is through Schema.org. If your website is hard-coded (not a CMS), Schema Org can help you choose and implement hundreds of schema templates.
You can choose from the hundreds of categories for schema and start optimizing your pages.
2. Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper
If you want a more beginner-friendly approach to creating schema markups, you can use Google’s Data Markup Helper. All you need to do is choose the type of schema you want and paste your page’s URL.
Once you are on the next screen, you will be given a preview of your website, and the option to fill missing tags.
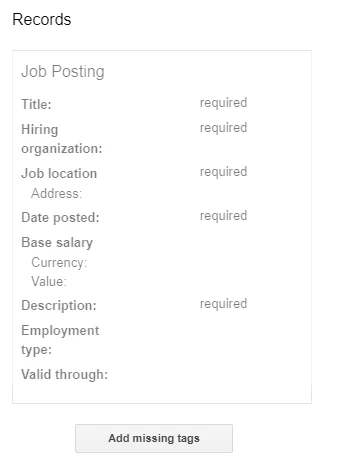
Make sure you add all the appropriate information and proceed to getting your code.
3. Use Schema WordPress Plugin
If you are using a CMS such as WordPress, you can generate schema automatically for all of your pages. In fact, you can also manually import, or add extra fields to your schema, giving you full control of changing information.
There are hundreds of SEO plugins, but the top ones used by most SEOs and website owners are Rank Math, Yoast, and All in One SEO.
Each of these plugins has many tutorials and tips-and-tricks videos, which could give you a head start in optimizing your schema markup.
How do I test my Schema and see if it is working?
Once you have added your schema markup to your website, it is very important to review if it is being rendered by search engine bots. 9 out of 10 times you may get the proper schema, but if you don’t, your Google Search Console will point to issues with Schema Markup.
To avoid recrawling, and dealing with issues, it is best to use a validator such as Schema Org’s Schema Validator.
Basically, their Schema Validator is used to review and tell if there is any kind of issue with the schema markup you have added to your website. This can be done by either sending in your web page or just copying and pasting your schema markup code.

If your schema is done properly, you should see the different schema fields without any errors or warnings. To be fair, if you see warnings there is nothing to worry about. Your schema will be shown, however, you may not get the expected results.